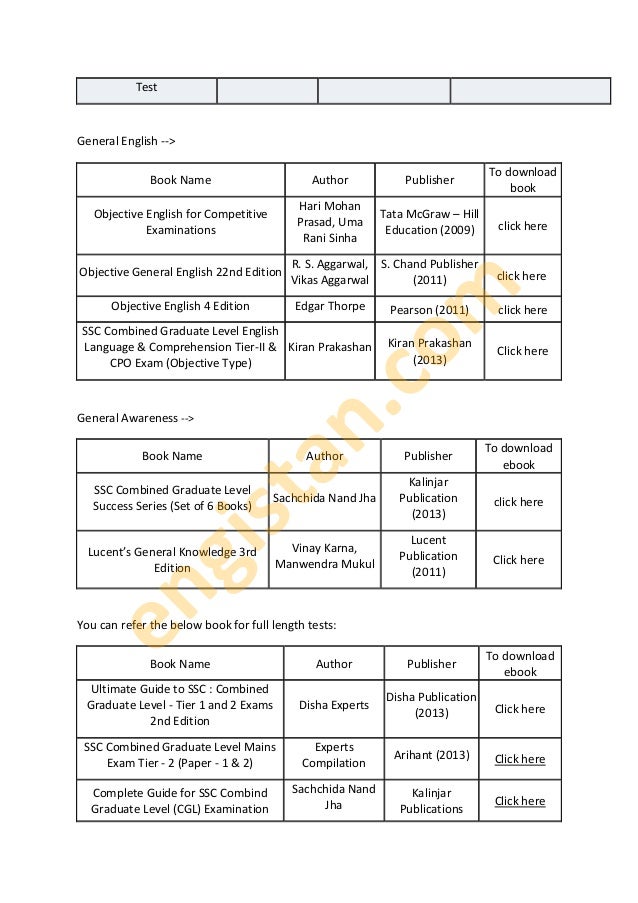
Objective English By Hari Mohan Prasad Ebook Store

Male and female from 17th- and 18th-century India This article contains. Roberto Fonseca Temperamento Rar. Without proper, you may see, misplaced vowels or missing conjuncts instead of Indic text. Yoga (;, योगः ) is a group of,, and practices or disciplines which originated in. There is a broad variety of yoga schools, practices, and goals in,, and.
Among the most well-known types of yoga are and. The origins of yoga have been speculated to date back to pre- traditions; it is mentioned in the, but most likely developed around the sixth and fifth centuries BCE, in ancient India's and movements. The chronology of earliest texts describing yoga-practices is unclear, varyingly credited to Hindu.
The date from the first half of the 1st millennium CE, but only gained prominence in the West in the 20th century. Hatha yoga texts emerged around the 11th century with origins in. Yoga gurus from India later introduced yoga to the West, following the success of in the late 19th and early 20th century.
In the 1980s, yoga became popular as a system of across the Western world. Yoga in Indian traditions, however, is more than physical exercise; it has a meditative and spiritual core. One of the six major orthodox schools of Hinduism is also called, which has its own epistemology and metaphysics, and is closely related to Hindu philosophy. Many studies have tried to determine the effectiveness of yoga as a complementary intervention for,,, and heart disease.
The results of these studies have been mixed and inconclusive. On December 1, 2016, yoga was listed by as an. Equated raja yoga with the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali. Yoga as described in the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali refers to Ashtanga yoga. The Yoga Sutras of Patanjali is considered as a central text of the Yoga school of Hindu philosophy, It is often called 'Rāja yoga', 'yoga of the kings,' a term which originally referred to the ultimate, royal goal of yoga, which is usually samadhi, but was popularised by Vivekananda as the common name for Ashtanga Yoga. Ashtanga yoga incorporates epistemology, metaphysics, ethical practices, systematic exercises and self-development techniques for body, mind and spirit.
About the Author: The book is written by Hari Mohan Prasad and Uma Rani Sinha. Hari Mohan Prasad has authored and co-authored eight books, some of which are General Studies For Civil Services Preliminary Examination, The Literary Heritage: A New Anthology of Prose and Short Story and A Handbook of Spotting. Objective english for competitive examination 5th ed. What type of questions asked complete guide with preparation tips – shortcut tricks objective english hari mohan prasad pdf download – formulas upsc has released written interview score of the toppers from civil service 2014 examination; from that, i've.
Its ( ) is same as the school. Both accept three reliable means to knowledge – perception ( pratyākṣa, direct sensory observations), inference ( anumāna) and testimony of trustworthy experts ( sabda, agama). Diana Palmer Love With A Long Tall Texan Pdf Files. Both these orthodox schools are also strongly. Unlike the Sāṃkhya school of Hinduism, which pursues a non-theistic/atheistic rationalist approach, the Yoga school of Hinduism accepts the concept of a 'personal, yet essentially inactive, deity' or 'personal god'. Along with its epistemology and metaphysical foundations, the Yoga school of Hindu philosophy incorporates ethical precepts ( and ) and an introspective way of life focused on perfecting one's self physically, mentally and spiritually, with the ultimate goal being kaivalya (liberated, unified, content state of existence).
A sculpture of, a celebrated 11th century yogi of Nath tradition and a major proponent of Hatha yoga. Hatha yoga, also called hatha, is a kind of yoga focusing on physical and mental strength building exercises and postures described primarily in three texts of: •, (15th century) •, author unknown (1500 or late 17th century) • by Gheranda (late 17th century) Many scholars also include the preceding Goraksha Samhita authored by of the 11th century in the above list.